51
Using the Notebook PC
4
IR Wireless Communication
The Notebook PC is equipped with a conveniently located Infrared (IR) Communication Port (see 2.
Knowing the Parts for location). The IR port comes with IrDA (Infrared Data Association) Serial
Infrared Data Link Version 1.1 compliance, that allows you to perform point-to-point wireless commu-
nications. You can use a FIR-specified application to transmit or receive data files with other systems
equipped with an infrared port. You must set these modes in the BIOS before you start to install the IR
driver and file-transferring applications. FIR (Fast Infrared) supports up to 4Mbps. See the Drivers and
Utilities Support CD User’s Manual for detailed setup instructions.
Guidelines for using IR communication
Follow the guidelines listed below when using the Infrared (IR) Communication:
• Make sure the IR Mode in the BIOS Setup is properly set to the mode you would like to use.
• The angle between two Infrared communication ports should not exceed ±15˚.
• The distance between the Notebook PC’s IR and target device IR should not exceed 20 inches (50 cm).
• Do not move either the Notebook PC or the other device during transmission of data.
• An error may occur if IR transmission is conducted with high levels of noise or vibration.
• Avoid direct sunlight, flashing incandescent light, florescent light, and other infrared devices such as
remote controls close to the infrared port.
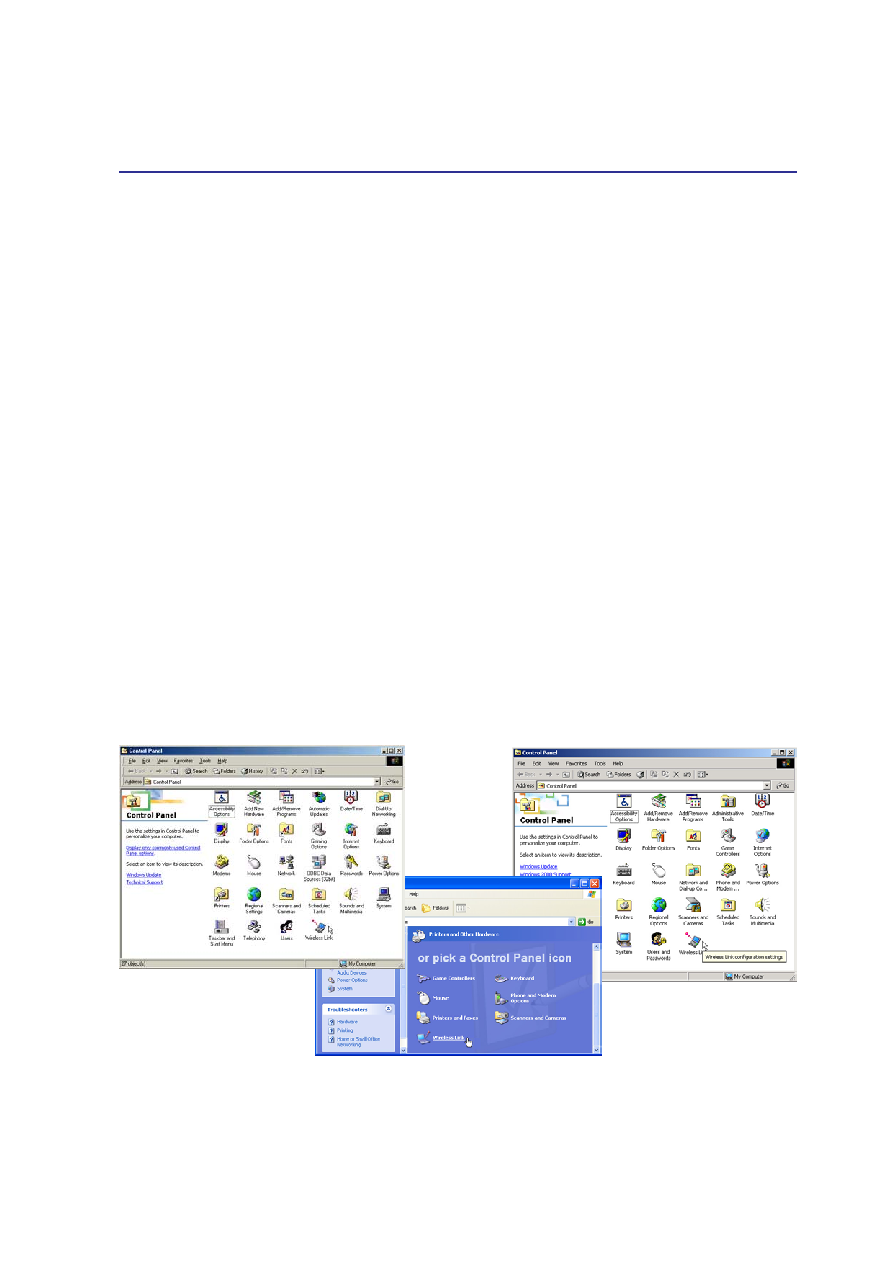
Enabling Infrared
MS Windows ME Infrared connection is called “Wireless Link” and should be enabled by default.
Look for the icon in the Control Panel. See the “Drivers and Utilities” manual for detailed setup in-
structions.
Windows ME
Windows 2000
Windows XP

