50
4. Using the Notebook PC
Using Battery Power
A fully-charged Li-Ion battery pack will provide the system approximately 2-4 hours of working power.
But the actual figure will vary depending on how you use the power saving features, your general work
habits, the Notebook PC’s CPU, main memory size, and the size of the display panel.
The “Battery Warning” beeps are automatically enabled in Windows 95/98 and will continually sound
when down to 10% (configurable in Windows 98) power. The processor will also be throttled down to
decrease power use.
In DOS, POWER.EXE must be enabled to use the Low Battery Warning Beep function in DOS. In
Windows 3.1, W31-APM must be enabled to use the battery warning beep feature. POWER.EXE must be
loaded via a DEVICE= line in CONFIG.SYS to report the status of the battery while using DOS or
Windows 3.x. POWER.EXE is not necessary when running Windows 95/98. For additional information,
see your DOS and Windows 3.1 User’s Manuals for details.
“Low Battery” condition (3% or less) will force the Notebook PC to enter suspend mode, regardless of
power management settings but the threshold is configurable in Windows 98.
NOTE: Battery Warning and Battery Low conditions will immediately stop upon appli-
cation of the power adapter.
NOTE: If you ignore the low battery warning, eventually the Notebook PC will enter
suspend mode (either Save-to-Disk or Save-to-RAM depending on BIOS setup).
WARNING! Save-to-RAM will not last long when the battery power is depleted.
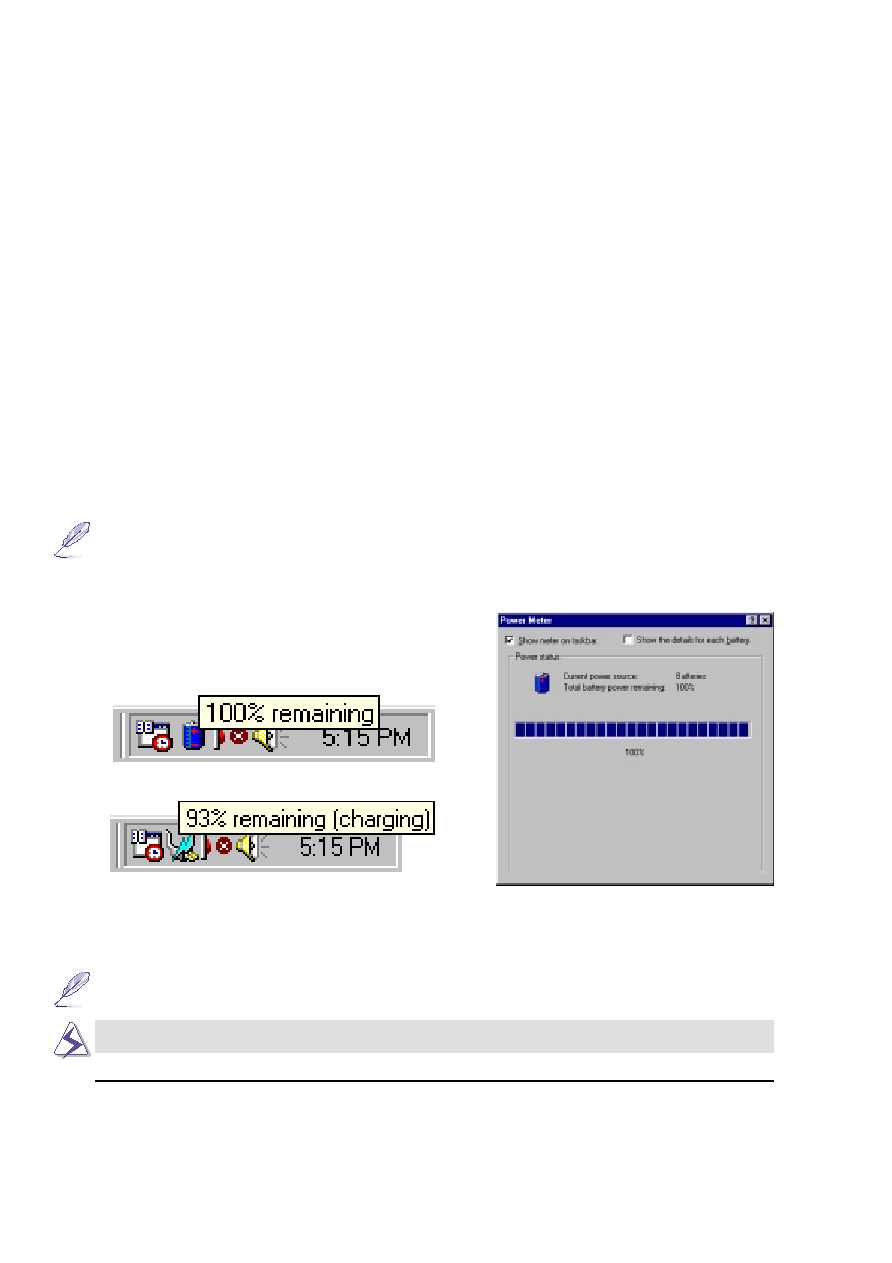
Power icon using battery.
Power icon using AC power. The charging
(lightning) icon appears over the “plug” icon if
the battery is not fully charged. When fully
charged, only the “plug” icon will remain.
Checking Battery Power
To check the remaining battery power, move your cursor
over the power icon. The power icon is a “battery” when
not using AC power and a “plug” when using AC power.
Double click on the icon for more information and settings.

