7
1.4 SNMP Overview
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is the most popular network management
protocol in the TCP/IP protocol suite. SNMP lets TCP/IP-based network management
clients exchange information about the configuration and status of nodes on a TCP/IP-
based Internet. The information available is defined by a set of managed objects referred to
as the SNMP.
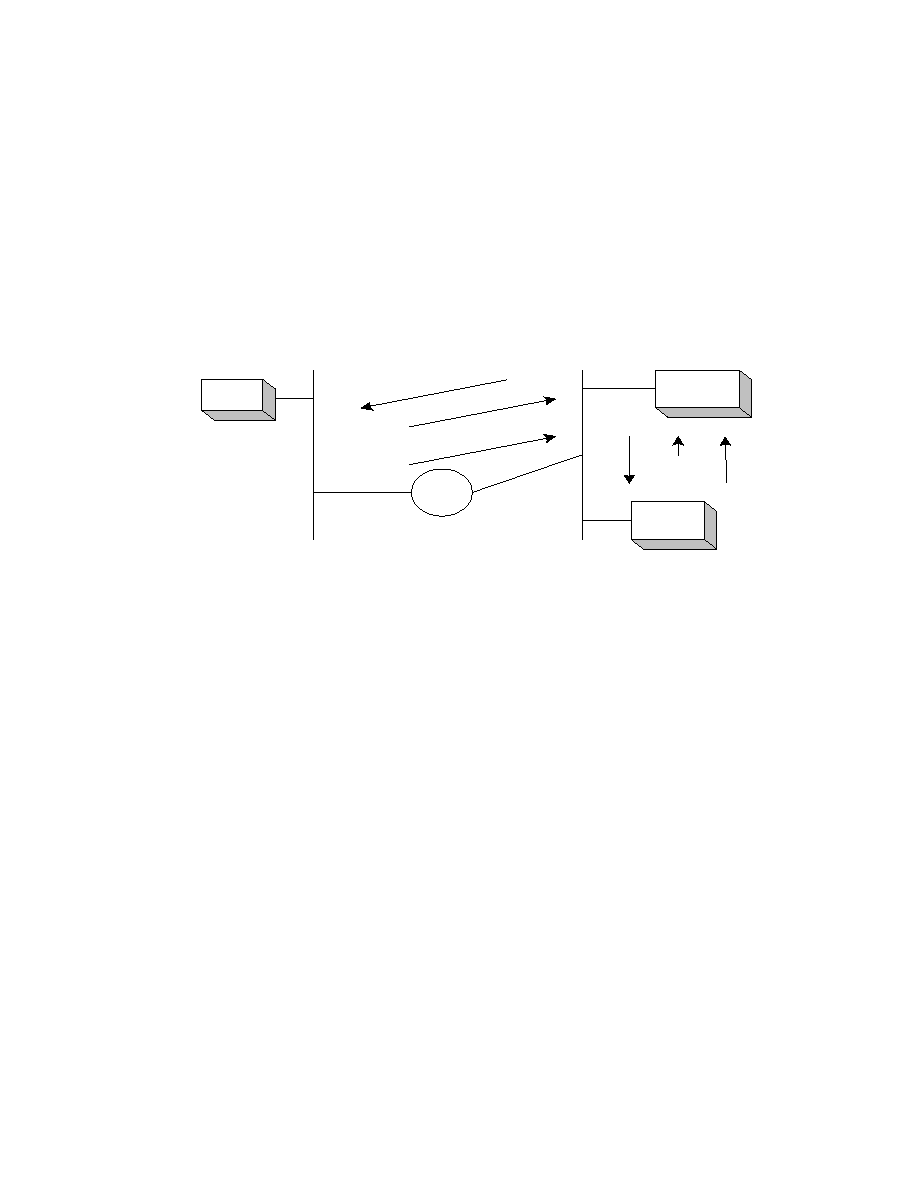
The example of SNMP in a network environment is illustrated as follows.
As mentioned above, we will introduce several terminology of SNMP.
Management Information Base (MIB). The subset of managed objects comprising the
TCP/IP portion of the MIB is maintained by each TCP/IP node. SNMP also generates trap
messages used to report significant TCP/IP events asynchronously to interested clients.
SNMP Get – let SNMP NMS get the value of attribute of managed system, such as fan
speed, working voltage and system temperature.
SNMP GetNext – allows the NMS to retrieve the next object instances from a table with
an agent.
SNMP Set – set the value of attribute of managed system, such as fan speed threshold,
working voltage threshold and system temperature threshold from SNMP NMS.
SNMP Response – be responsible for the response of SNMP GET, SNMP GETNext and
SNMP Set.
SNMP Trap – managed computer system can inform the NMS of some event ( when the
interested attributes, such as fan/voltage/temperature, over or lower the thresholds )
asynchronously.
ASMA
Internet
SNMP
Management
ASMA
Ethernet
EThernet
Set/Get
Get/Set
Response
Trap
Set/Get
SNMP Management means a server can control other clients via
SNMP. (like HP Openview )
Set/Get
Response
Trap

